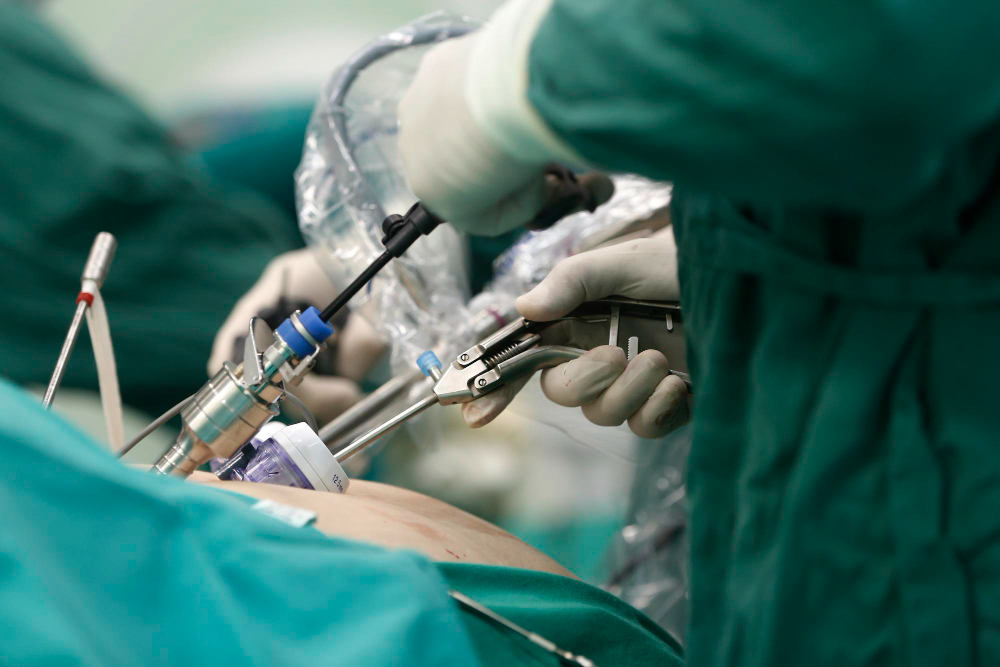
What is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive surgery to remove the gallbladder. Doctors often call it keyhole surgery. This procedure uses small cuts and a camera to guide the surgeon. Most people need this surgery because of gallstones or gallbladder disease. Unlike open surgery, laparoscopic cholecystectomy usually means less pain and a quicker recovery. Many patients search for “minimally invasive gallbladder removal” or “gallbladder surgery recovery” to learn more about this safe and common operation.
Why is it Performed? (Indications)
Doctors recommend laparoscopic cholecystectomy for several reasons. Most often, it is done to treat:
Sometimes, people have repeated stomach pain or digestive issues. In these cases, doctors may suggest this surgery. According to the CDC, gallstones are a common reason for gallbladder removal.
How is the Procedure Done?
First, you will receive anesthesia, so you sleep during the surgery. Next, the surgeon makes 3 to 4 small cuts in your belly. Through these cuts, they insert a tiny camera and special tools. The camera sends images to a screen, helping the doctor see inside. Then, the surgeon carefully removes the gallbladder. After that, the small cuts are closed with stitches or surgical glue. Most surgeries last about one to two hours. Because it is minimally invasive, you may go home the same day.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
This type of gallbladder surgery offers many advantages. For example, patients often experience:
Additionally, most people recover more quickly compared to open surgery. The World Health Organization supports minimally invasive surgery for its safety and effectiveness.
Risks and Possible Complications
Although laparoscopic cholecystectomy is safe, all surgeries have risks. Some possible complications include:
However, serious problems are rare. Your surgeon will discuss these risks with you before the operation. If you notice fever, severe pain, or yellowing of the skin after surgery, contact your doctor right away.
Recovery and Aftercare Tips
Most people recover quickly after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Here are some helpful tips for a smooth recovery:
Usually, you can return to work or school within one to two weeks. However, everyone heals at their own pace. If you have questions about your recovery, ask your healthcare team.
Prevention and Lifestyle Guidance
After gallbladder removal, you can still live a healthy life. To help prevent future digestive problems, consider these tips:
For most people, these changes help the body adjust after surgery. If you notice ongoing digestive issues, talk to your doctor for advice.
In summary, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a safe and effective way to treat gallbladder problems. For more information or personalized advice, consult a qualified surgeon about laparoscopic cholecystectomy.